April 13, 2023
Actionable Data Insights for Improved Business Results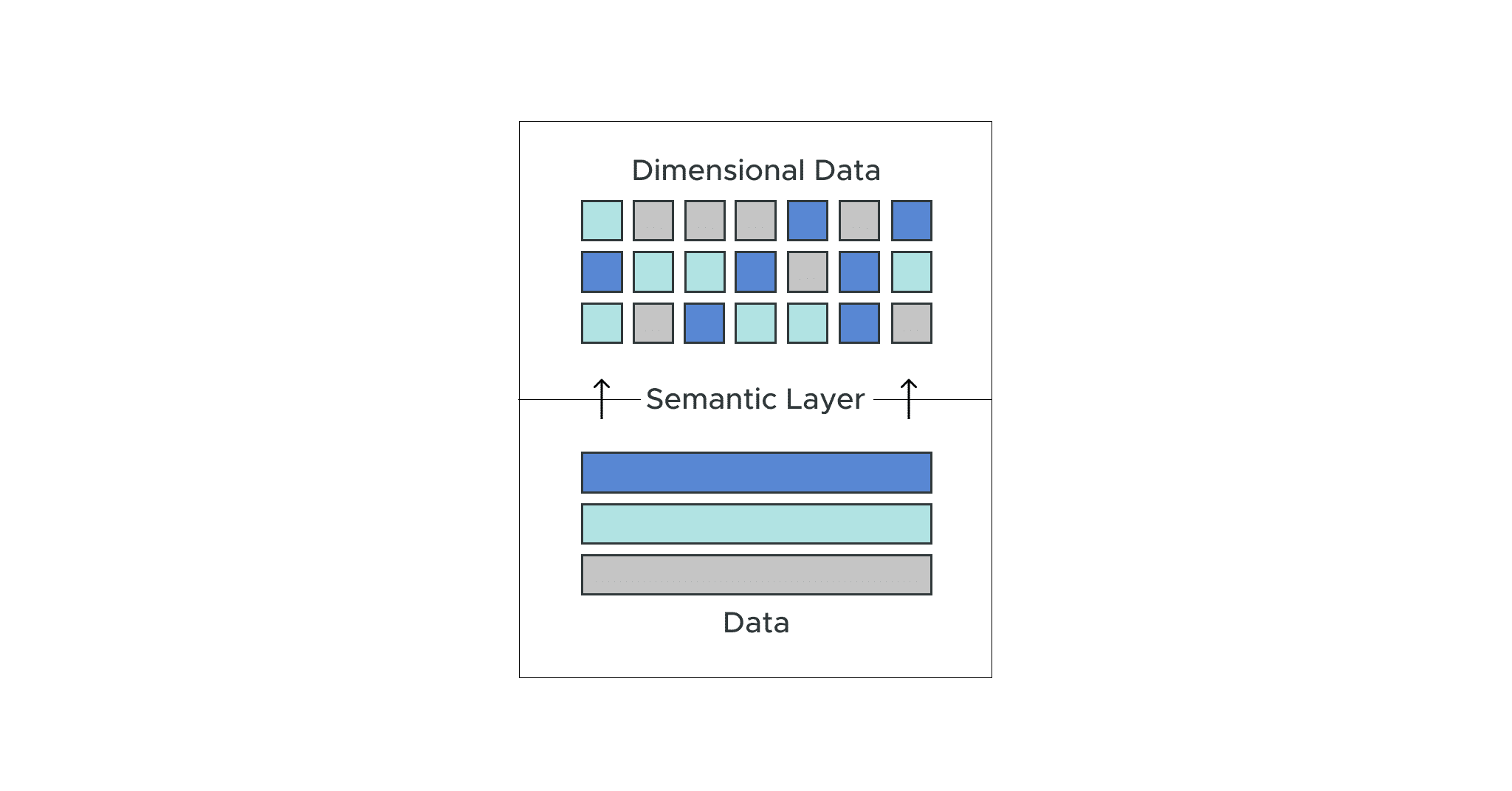
This is a series of blog posts based on AtScale TechShorts – an interactive video series to build a foundational understanding of the core building blocks of the universal semantic layer in the modern data stack. Here are links to the first post, The Semantic Layer and its Role in the Modern Data Stack, and second post, The Metric Store and its Role in the Modern Data Stack, in the series.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, data and analytics have become indispensable tools for informed decision-making. As organizations increasingly centralize their data on cloud platforms and leverage multiple analytics tools, the role of the semantic layer has grown in importance. Dimensional Data Modeling is a core capability of the semantic layer that empowers businesses to make sense of their data. In this blog post, we’ll delve into why dimensional data modeling is a crucial component of the semantic layer and explore the key must-haves for a robust semantic data model in the modern data stack.
The Semantic Layer: Connecting Data and Insights
The semantic layer serves as a vital bridge between complex data sources and end-users seeking actionable insights. It accomplishes this by offering a well-defined, business-friendly layer that provides a single version of truth, simplifying data access, ensuring data consistency, and promoting data-driven decision-making.
Dimensional Data Modeling: The Core of the Semantic Layer
At the heart of the semantic layer platform is the semantic data model. Dimensional data modeling involves creating business-oriented, logical data models directly mapped to the physical data structures in data warehouses or lakehouses. It presents a logical view of the underlying databases and schemas without physically moving the data. This organization of data relies on dimensional schemas, including measures (facts) and dimensions (categories or attributes and their hierarchies), resulting in a consolidated view organized in business terms.
Four Key Criteria of a Semantic Data Model
To understand why dimensional data modeling is a core capability of the semantic layer, let’s explore the essential features that a modern semantic data model should possess:
- Flexible and Advanced Multi-Dimensional Modeling Framework
Multi-dimensional data is a cornerstone of effective analytics. It enables users to analyze data from various angles, providing a comprehensive view. The Semantic Layer should enable multi-dimensional modeling on top of cloud data without physically moving or extracting data, empowering business users to perform traditional OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) analysis on their cloud data. - Welcome All Data Personas
A modern semantic data model should cater to the diverse needs of different data personas, such as BI developers, data engineers, citizen data scientists, and BI analysts. It should provide flexibility for both code-first data modelers and those who prefer a no-code, visual approach to data modeling. - Support Composable and Versionable Semantic Objects
Taking inspiration from Object-Oriented Programming, a modern semantic model should enable data modelers to abstract real-world business entities into composable and versionable objects. This approach promotes modularity, reuse, flexibility, and effective development, allowing metrics, dimensions, and entire models to be shared, composed, and versioned with Git integration. - Be Intelligent and Serve 3rd Party Semantic Models
Data can be messy, and semantic modeling should be intelligent, providing real-time guidance on modeling issues. Furthermore, the Semantic Layer should seamlessly integrate and serve other 3rd party semantic models, facilitating a unified hub for all semantic models within an organization for BI and analytics consumption.
In the modern data stack, dimensional data modeling stands as a core capability of the semantic layer. It provides a flexible, multi-dimensional modeling framework and welcomes all data personas. Additionally, it supports composable and versionable semantic objects and exhibits intelligence while accommodating 3rd party semantic models. This empowers organizations to harness the full potential of their data.As businesses continue to rely on data and analytics for strategic decisions, mastering Dimensional Data Modeling is essential to stay competitive in today’s data-driven landscape.
To learn more about the semantic layer in the modern data stack, watch the entire TechShorts video series.
ANALYST REPORT